What Is the Most Important Equipment for Blood Banking?
Blood donations are lifesaving and used in transfusions by health care facilities worldwide. However, before blood components can be used, they must be tested and stored in blood banks. Blood banks test blood to ensure it is safe for use. They also keep blood components before transporting them to the blood banks of health care facilities.
Blood bank equipment is essential, as it protects and maintains blood components. Refrigerators, freezers and thawing equipment help create a cold chain that prevents the degradation of blood components.
What Is the Difference Between Blood Donation, Blood Manufacturing and Blood Banking?
Blood donation is the process by which a phlebotomic collection of whole blood or an apheresis collection of select blood components is obtained from a willing blood donor who passed screening criteria. The blood or blood components are used in transfusions and transfusion medicine. Apheresis collections involve using a separation device containing a special centrifuge that separates blood components while the blood is being collected. The selected component goes into a collection bag, and the rest of the blood is returned to the donor's circulation. This process is similar to hemodialysis, in which blood is filtered outside a patient's body and returned to the patient's circulation free of metabolic waste.
Blood banking is the process of testing and storing donor whole blood and blood components to be used for transfusions and other medical procedures. Blood banking also involves the testing of patient blood collections to ensure safe transfusions. Blood banking occurs in a laboratory where blood is typed and tested for infectious diseases to ensure it is safe for medical procedures. Typing and testing blood is crucial and is one of the first stages of blood banking after donation or collection. Some of the procedures performed on blood by serologic and molecular methods include:
- ABO typing
- Rh factor testing
- Antibody screening
- Hepatitis B and C testing
- Testing for STDs, specifically syphilis and HIV
- Infectious disease testing, including West Nile Virus and Chagas Disease
While testing confirms whether blood is safe for use and is properly typed, blood manufacturing is the process by which whole blood is separated into its four major components: red blood cells, plasma, platelets and cryoprecipitate. Testing and manufacturing are done concurrently, largely through centrifugation and the layering of components. However, the fourth major component, cryoprecipitate, requires freezing of plasma and thawing under refrigeration to derive.
Additional blood manufacturing that can be done includes blood and platelet irradiation, pathogen inactivation and further processing to derive minor blood components, such as clotting factors.
Each component is vital for medical procedures. Red blood cells are the most commonly used component and are used in blood transfusions. Plasma is another essential blood component given to shock, burn and trauma patients. It can help boost patients' blood volume, improving blood clotting. The blood and its various components are stored in the blood bank laboratory before being transported to various health care facilities.
Why Is Having the Right Equipment Important?
Blood and its various components can degrade quickly when left at room temperature and exposed to the elements. Blood components must be placed in cold storage as soon as possible to maintain their integrity, prevent degradation and limit exposure to bacteria. Blood bank equipment is designed specifically for this use. Blood refrigerators, freezers and transport systems are intended to protect blood components from the elements so they can be safely tested and eventually used in transfusions.
It is essential to remember that each blood bank and health care facility is different with its own processes and space requirements. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to equipment. Blood bank equipment requires a tailored approach. Each blood bank requires equipment that suits their specific needs. If a blood bank only handles a limited amount of blood, investing in large refrigerators and freezers can take up space and resources. Alternatively, if they are only involved in short-term storage, they will require standard freezers rather than ultra-low-temperature freezers.
What Is Important Blood Banking Equipment?
Using the proper blood bank equipment is essential for maintaining the condition of the blood and the blood components. Blood bank equipment ranges from collection equipment to storage facilities, freezers and refrigerators. Blood bank equipment is also essential for safely transporting blood and blood components to health care facilities and between blood banks.
Blood Collection Equipment
The first step in blood donation and banking is collecting the blood, which requires various types of equipment, from needles to tubing and blood bags. One of the most important pieces of equipment when collecting whole blood is the blood collection mixer or scale. Blood scales provide essential information when collecting blood, including the target blood volume, current blood volume, elapsed time, collection start time and the fullness percentage.
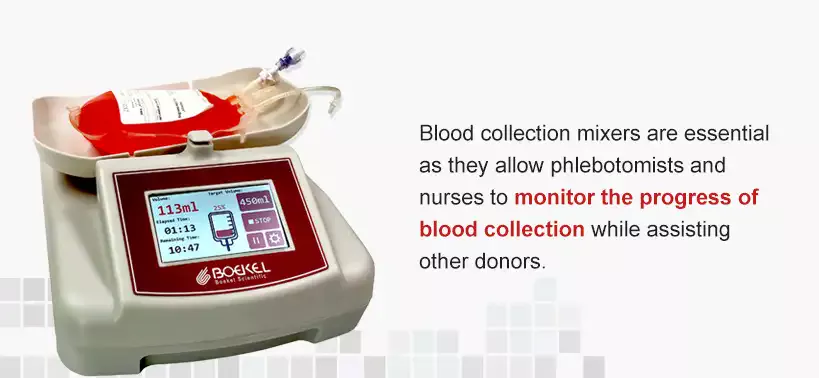
Blood collection mixers are essential as they allow phlebotomists and nurses to monitor the progress of blood collection while assisting other donors. They usually have alarms that notify the relevant practitioner when the collection process is nearing its end or is completed as well as errors in the process such as low-flow rate and equipment failures.
Platelet Storage Equipment
Platelet storage can be challenging, as platelets need to be stored in a temperature-controlled environment. They also need to be agitated to ensure proper oxygenation. Platelet storage equipment is specifically designed to provide these two functions. Typically, they have multiple shelves where platelets can be stored. These shelves are also designed to move in specific ways to agitate platelets as needed. Additionally, they are engineered to create laminar airflow around the platelets.
Platelet storage equipment also provides crucial information on the state of the platelets, including the temperature. Some models are also available with inventory management systems that can help reduce platelet wastage by tracking expiration dates. There are different sizes of platelet storage equipment, from small benchtop units to larger floor-standing units. The size you choose will depend on your laboratory's needs and space.
Plasma Thawing Equipment
Plasma is frozen to store and transport safely. It is also frozen to extend its shelf life. Fresh frozen plasma can be safely stored for 12 months before use. Its shelf life can be extended to nearly seven years if stored in colder conditions. Plasma must be thawed before it is used, and thawing plasma can be a delicate and time-consuming process.
Plasma thawing equipment can make the thawing process significantly easier as it controls the thawing temperature and provides agitation to ensure plasma is thawed correctly. The equipment also has safety features to ensure the plasma remains uncontaminated while thawing. It also has alarms to signal when the cycle is complete, allowing employees to work on other projects while the plasma thaws.
Other Important Blood Banking Equipment
Consider other essential blood banking equipment:
- Blood bank refrigerators: Blood and its various components need to be stored at specific temperatures. Blood bank refrigerators are essential to keeping blood and other components safely refrigerated. They are intended to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the unit so that all the components stored are kept at similar temperatures while a safety thermostat prevents freezing. The temperatures in a blood refrigerator usually range from 2 degrees C to 4 degrees C.
- ULT freezers:Ultra-low-temperature (ULT) freezers can reach temperatures up to minus 86 degrees C and store glycerolized, frozen red blood cells, plasma and other blood components. ULT freezers are essential for the long-term storage of components. The low temperatures protect the integrity of the various components by helping reduce their exposure to high temperatures.
- Contact shock freezers: Freezing blood, plasma and other components is essential in blood banking, as it helps protect the components and maintain their integrity. The faster blood components are frozen, the better. The freezing should also be uniform. The best way to freeze blood components is with contact shock freezers, which provide fast, uniform freezing.
- Blood transport systems: Blood and its various components will eventually be transported from a blood center to other health care facilities, blood banks or laboratories. They must be transported in medical transport boxes that maintain the cold chain and preserve the integrity of the components. Medical transport systems must always maintain a constant temperature as they are moved between different facilities.
Innovative Lab and Blood Banking Equipment From Boekel Scientific
Blood banks require specific equipment explicitly designed to protect blood components. Boekel Scientific is one of the world's leading designers, manufacturers and suppliers of blood banking equipment. For over 150 years, we have been creating innovative blood bank equipment that can help protect blood components and make blood banking safer.
Discover our wide range of blood bank equipment, or request a quote from our team today!


